Biomedical Engineering cuts across and through every length and breadth of all clinical settings - from the simple cotton used to major equipment like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine. Amongst the many evolutions of Biomedical Engineering is the Cell Saver. In Ghana this technology is found in just one or two hospitals. Let us break down the importance of this system.
Blood transfusion in every clinical setting is an indispensable procedure done to save lives. But too much blood transfusion even with the same blood group can be very harmful and may lead to complications even to death.
So, there is the need to get a system that can salvage patients own blood, process it, and return it to the patient in a safe way.
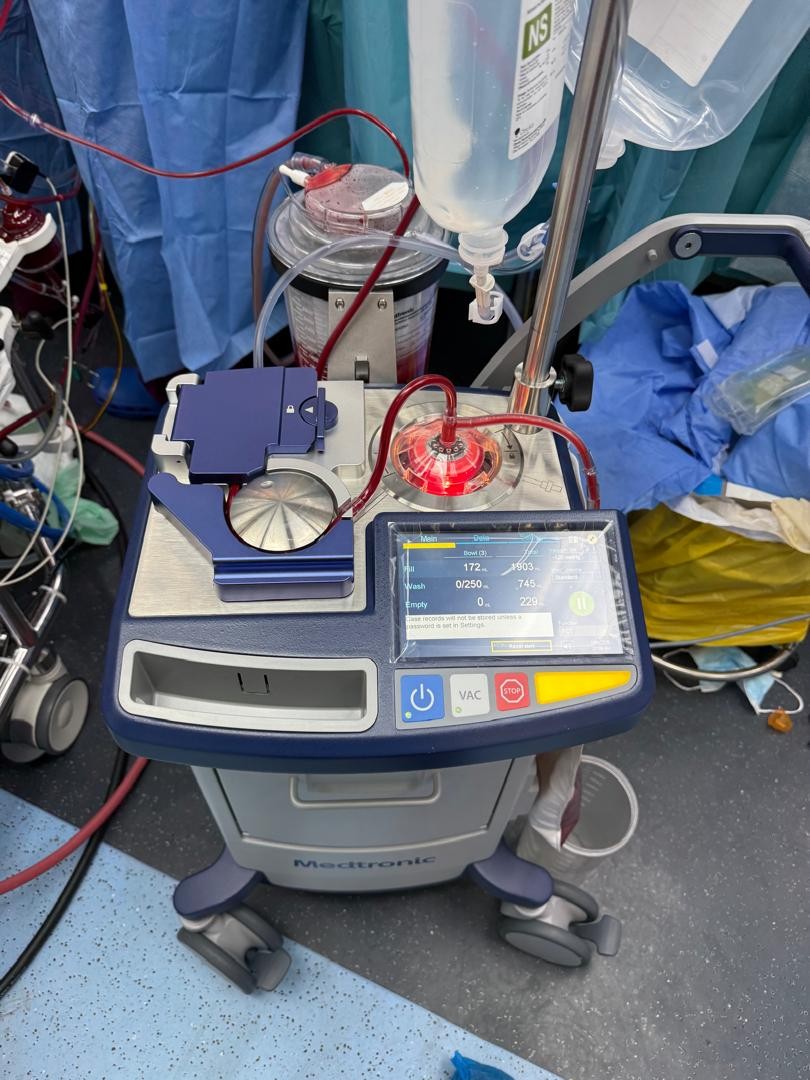
This therefore leads us to a system called Cell Saver. This system is used for collecting, washing, concentrating, and re-infusing a patient's own blood during surgery.
A cell saver, or intra-operative blood salvage, is a medical device that collects, washes, and re-infuses a patient's own blood lost during surgery. This process reduces the need for donated blood transfusions, eliminating the risks of disease transmission and allergic reactions associated with allogeneic blood. It is commonly used in surgeries with significant anticipated blood loss, such as cardiac, orthopaedic, and major trauma procedures.
How it works
- Blood lost during surgery is collected and sent to the cell saver machine.
- The machine uses centrifugal force to spin the blood.
- This separates the red blood cells from plasma, platelets, and other contaminants like air bubbles or fat particles.
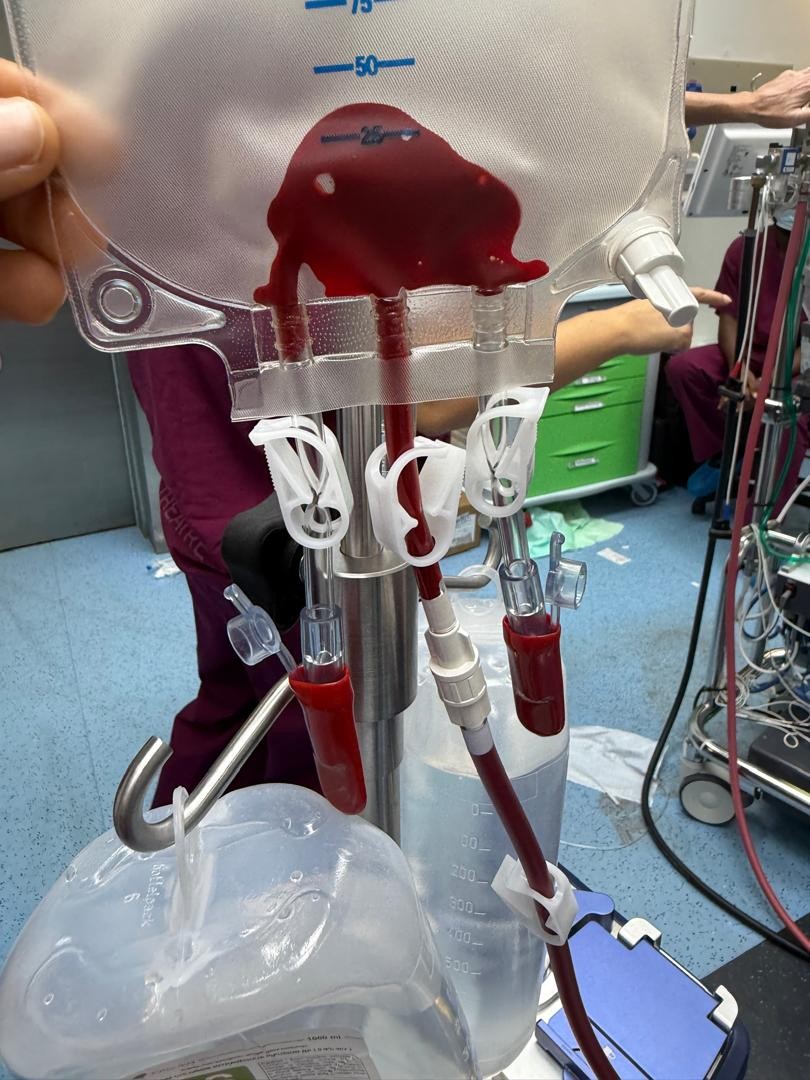
- The red blood cells are washed with a saline solution.
- The cleaned, concentrated red blood cells are then collected in a bag for re-infusion into the patient.
Benefits
- Reduces need for donor blood: Minimises the use of allogeneic blood, which can be in short supply.
- Eliminates risks of donor blood: Prevents risks of disease transmission (e.g., HIV, Hepatitis B/C), allergic reactions, and immune suppression.
- Improves blood properties: The patient's own blood is re-infused immediately, avoiding the compromised oxygen-carrying capacity of stored donor blood.
- Suitable for specific patients: Useful for patients with rare blood types, multiple antibodies, or those who cannot receive donor blood for religious reasons (e.g., some Jehovah's Witnesses).
Common applications
- Cardiac surgery
- Orthopaedic surgery (e.g., joint replacements, spinal fusions)
- Major trauma and emergency care
- Vascular surgery
- Obstetrics and gynaecology (e.g., cesarean sections)
- Fat grafting procedures like a BBL (Brazilian Butt Lift)